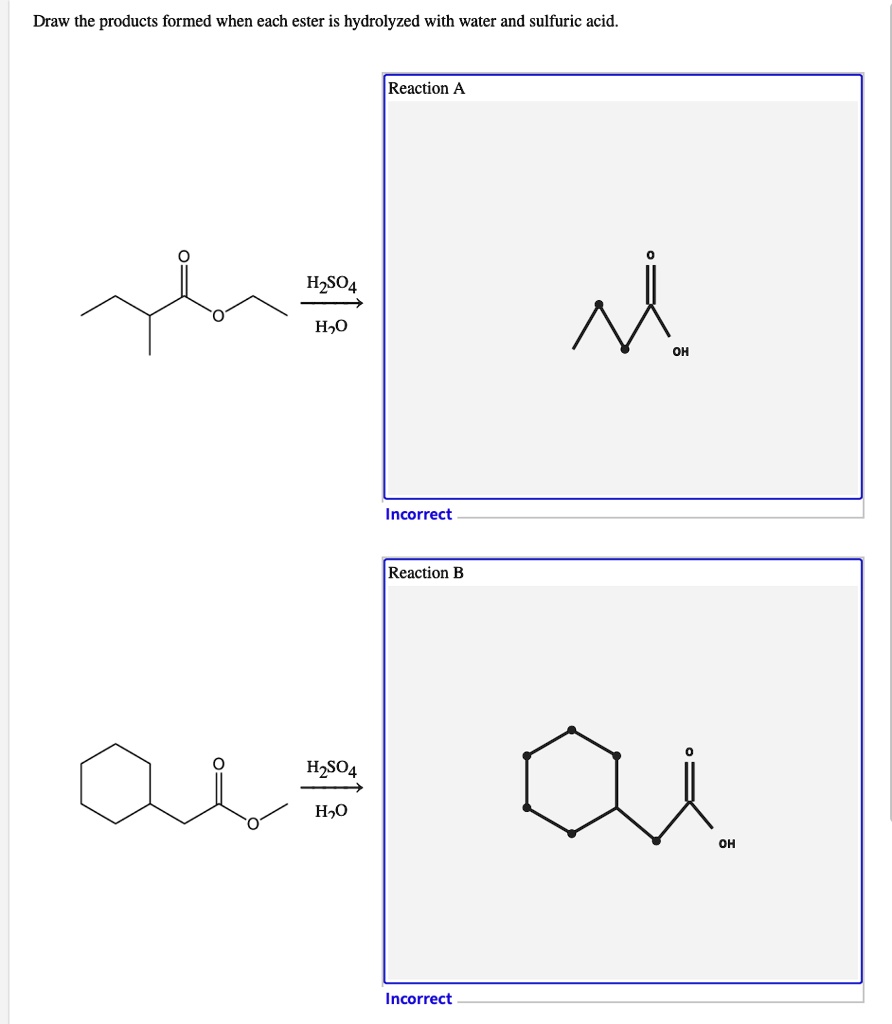
Draw The Products Formed From The Ester Hydrolysis Reaction Shown
Draw The Products Formed From The Ester Hydrolysis Reaction Shown - In typical reactions, the alkoxy (or′) group of an. It means cleavage of chemical bonds of compound through the addition of water. As shown in figure 21.8, ester hydrolysis occurs through a typical nucleophilic acyl substitution pathway in which hydroxide ion is the nucleophile that adds to the ester carbonyl group to give. Draw the products formed when each ester is hydrolyzed with water and sulfuric acid. The conditions in the solution would push the reaction forward. This page looks in detail at the mechanism for the hydrolysis of esters in the presence of a dilute acid (such as hydrochloric acid or.
There are two advantages of doing this rather than. The ester is heated under reflux with a dilute alkali like sodium hydroxide solution. Acid catalyzed hydrolysis of esters. In typical reactions, the alkoxy. Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed.
Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester. Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed. Part a draw the products formed from the ester hydrolysis reaction shown. Ester hydrolysis or hydrolysis of an ester is the reaction of an ester with water in an acidic or basic medium to yield alcohol and carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt. Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester.
Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester. This is the usual way of hydrolyzing esters. Ester hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which an ester reacts with water to produce a carboxylic acid and an. If there is an excess of butanol in acid while there is only a limited amount of ester, you would see. This.
In typical reactions, the alkoxy. Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester. If there is an excess of butanol in acid while there is only a limited amount of ester, you would see. Draw the products formed when each ester is hydrolyzed with water and sulfuric acid. As shown in figure 21.8, ester hydrolysis occurs through a.
H,0 hydrolysis draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the tools (for. Ester hydrolysis or hydrolysis of an ester is the reaction of an ester with water in an acidic or basic medium to yield alcohol and carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt. It means cleavage of chemical bonds of compound through the addition of water. Draw the.
As shown in figure 21.8, ester hydrolysis occurs through a typical nucleophilic acyl substitution pathway in which hydroxide ion is the nucleophile that adds to the ester carbonyl group to give. Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed. There are 4 steps to solve this one. H,0 hydrolysis draw the molecule on the canvas by.
Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed. In typical reactions, the alkoxy (or′) group of an. In typical reactions, the alkoxy (or′) group of an ester is replaced by. Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester. The conditions in the solution would push the reaction forward.
As shown in figure 21.8, ester hydrolysis occurs through a typical nucleophilic acyl substitution pathway in which hydroxide ion is the nucleophile that adds to the ester carbonyl group to give. Acid catalyzed hydrolysis of esters. H,0 hydrolysis draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the tools (for. In typical reactions, the alkoxy. The conditions in the.
Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed. There are 4 steps to solve this one. Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed. It means cleavage of chemical bonds of compound through the addition of water. During hydrolysis reaction with pure water is slow and usually not used,.
This page looks in detail at the mechanism for the hydrolysis of esters in the presence of a dilute acid (such as hydrochloric acid or. H,0 hydrolysis draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the tools (for. Part a draw the products formed from the ester hydrolysis reaction shown. If there is an excess of butanol in.
Part a draw the products formed from the ester hydrolysis reaction shown. As shown in figure 21.8, ester hydrolysis occurs through a typical nucleophilic acyl substitution pathway in which hydroxide ion is the nucleophile that adds to the ester carbonyl group to give. Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed. Identify the products of a.
This is the usual way of hydrolyzing esters. Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester. Ester hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which an ester reacts with water to produce a carboxylic acid and an. In typical reactions, the alkoxy. There are two advantages of doing this rather than.
Draw The Products Formed From The Ester Hydrolysis Reaction Shown - Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester. Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester. Part a draw the products formed from the ester hydrolysis reaction shown. The conditions in the solution would push the reaction forward. H,0 hydrolysis draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the tools (for. In typical reactions, the alkoxy (or′) group of an. Acid catalyzed hydrolysis of esters. The alkaline hydrolysis of esters actually involves reaction with hydroxide ions, but the overall result is so similar that it is lumped together with the other two. As shown in figure 21.8, ester hydrolysis occurs through a typical nucleophilic acyl substitution pathway in which hydroxide ion is the nucleophile that adds to the ester carbonyl group to give. In typical reactions, the alkoxy (or′) group of an.
There are 4 steps to solve this one. This is the usual way of hydrolyzing esters. Draw the products formed when each ester is hydrolyzed with water and sulfuric acid. Ester hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which an ester reacts with water to produce a carboxylic acid and an. Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester.
Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed. During hydrolysis reaction with pure water is slow and usually not used,. Part a draw the products formed from the ester hydrolysis reaction shown. In typical reactions, the alkoxy (or′) group of an.
This page looks in detail at the mechanism for the hydrolysis of esters in the presence of a dilute acid (such as hydrochloric acid or. Draw the products formed when each ester is hydrolyzed with water and sulfuric acid. Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed.
Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester. Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed. In typical reactions, the alkoxy.
During Hydrolysis Reaction With Pure Water Is Slow And Usually Not Used,.
Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed. Ester hydrolysis or hydrolysis of an ester is the reaction of an ester with water in an acidic or basic medium to yield alcohol and carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt. The ester is heated under reflux with a dilute alkali like sodium hydroxide solution. Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed.
Esters Are Neutral Compounds, Unlike The Acids From Which They Are Formed.
Draw the products formed when each ester is hydrolyzed with water and sulfuric acid. Ester hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which an ester reacts with water to produce a carboxylic acid and an. As shown in figure 21.8, ester hydrolysis occurs through a typical nucleophilic acyl substitution pathway in which hydroxide ion is the nucleophile that adds to the ester carbonyl group to give. The conditions in the solution would push the reaction forward.
If There Is An Excess Of Butanol In Acid While There Is Only A Limited Amount Of Ester, You Would See.
Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester. Part a draw the products formed from the ester hydrolysis reaction shown. In typical reactions, the alkoxy (or′) group of an. In typical reactions, the alkoxy.
The Alkaline Hydrolysis Of Esters Actually Involves Reaction With Hydroxide Ions, But The Overall Result Is So Similar That It Is Lumped Together With The Other Two.
There are two advantages of doing this rather than. In typical reactions, the alkoxy (or′) group of an ester is replaced by. This is the usual way of hydrolyzing esters. There are 4 steps to solve this one.